
Briefly
- Quantum computer systems can generate "certifiably random" numbers which might be actually unhackable, in contrast to conventional computer systems.
- Researchers used a 56-qubit quantum pc to create 70,000+ verified random bits that may require large supercomputing energy to pretend.
- True randomness may revolutionize safety for encryption, blockchain, and digital signatures, although implementation stays difficult.
A group of researchers from JP Morgan Chase, Quantinuum, and others has proven that quantum computer systems can produce “certifiably random” numbers, doubtlessly bettering how we safe all the pieces from banking to voting methods.
It seems that the random numbers some pc packages use aren’t so random.
In cryptography—the tech underlying two-factor authentication and passkeys as an example—random numbers are generated to safe methods from hackers. However conventional computer systems sometimes use algorithms that solely mimic randomness, and are literally based mostly on an algorithmic components, making them doubtlessly hackable if somebody figures out the sample.
"Think about now we have an inventory that begins with 'Ace of Diamonds' and ends 53 objects later with a Joker. To shuffle this on a pc, I’d use the Knuth Shuffle, which is a widely known algorithm. The issue is that if we run the algorithm on our ordered 'deck' with the identical 'seed' once more, we get the identical 'shuffled' output," Clyde Williamson, senior product safety architect at information safety agency Protegrity, informed Decrypt.
The breakthrough, revealed in Nature, demonstrated that the group was capable of obtain licensed randomness, which means that the numbers had been demonstrably random and unhackable.
Utilizing Quantinuum's 56-qubit trapped-ion pc, the analysis group generated over 70,000 licensed random bits in a course of that took mere seconds per bit to create, however would require 4 of the world's prime supercomputers working nonstop to pretend—as in, producing the same sequence with a mathematical components that may make the method appear deterministic.
The numbers had been later verified by a gaggle of supercomputers able to proving there was not a mathematical algorithm concerned of their era.
The achievement marks a significant step past earlier quantum computing claims that usually concerned contrived duties with little real-world worth. This time, the applying tackled a elementary problem in cybersecurity: creating random numbers which might be provably unbiased and unpredictable.
"Conventional random quantity era faces two main challenges: the potential for manipulation or predictability in entropy sources, and weaknesses within the algorithms utilized by pseudo-random quantity turbines to develop that entropy," Kee Jefferys, co-founder of encrypted messaging app Session—and co-author of the proof-of-stake privateness coin Oxen’s Whitepaper—informed Decrypt. "Quantum randomness introduces a essentially totally different entropy supply, rooted within the intrinsic unpredictability of quantum mechanical processes."
The power to generate true randomness relies on the peculiar world of quantum mechanics. Quantum computer systems use qubits reasonably than binary bits, permitting them to exist in a number of states concurrently due to a phenomenon referred to as superposition—a state that was viralized by Schrodinger's well-known clarification positing a cat that’s alive and lifeless on the similar time inside a field.
When measured, these qubits produce genuinely random outcomes—not as a result of we lack info, however as a result of nature itself hasn't decided the result till remark happens. In different phrases, the cat lives or dies solely when anyone opens the field.
(Tl;dr: Quantum computer systems are higher at producing actually random numbers as a result of quantum mechanics is essentially indeterministic—whereas classical computer systems are deterministic machines pretending to be random.)
The protocol works by a intelligent back-and-forth between quantum and classical computing. First, the quantum pc performs so-called random circuit sampling, a technique utilized in quantum computing to benchmark and exhibit quantum benefit—that’s, performing a activity sooner on a quantum pc than any recognized classical pc can.
It generated outputs in about two seconds every. Then, classical supercomputers at Argonne and Oak Ridge Nationwide Laboratories spent 18 hours verifying these outputs utilizing a way referred to as cross-entropy benchmarking, which confirmed they couldn't have been produced by classical means.
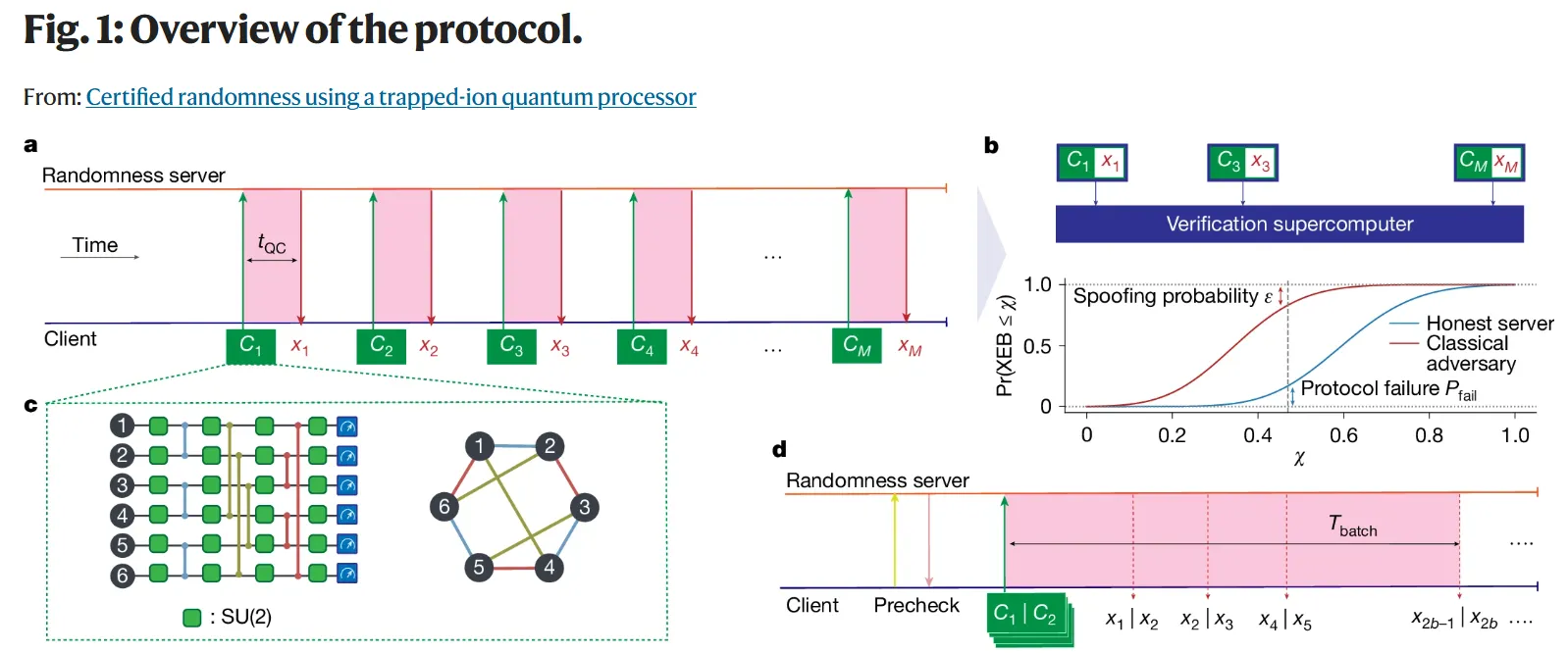
This verification course of ensures that the random numbers weren't manipulated by anybody—not even by the quantum pc's producers. This has not been achieved earlier than, and marks the primary time a general-purpose quantum pc has been used to generate publicly verifiable, licensed quantum randomness at scale.
The stakes for getting randomness proper are excessive. Duncan Jones, head of cybersecurity at Quantinuum—one of many analysis labs concerned within the research alongside JP Morgan—pointed to a number of dramatic examples of what occurs when randomness fails.
"In 2010, Sony's PlayStation breach occurred as a result of the builders failed to make use of robust random quantity era, permitting attackers to show the personal cryptographic key," Jones informed Decrypt. "Extra not too long ago, the Polynonce assault (2014-2023) exploited weak Bitcoin pockets randomness, resulting in the theft of 140 Bitcoin (~$10M)."
Felix Xu, CEO of ARPA Community, highlighted one other pricey incident: "A infamous instance is the 2013 Android SecureRandom vulnerability, the place weak entropy in Bitcoin pockets functions allowed attackers to steal personal keys, draining hundreds of thousands of {dollars} in Bitcoin."
“Equally, in 2019, a flawed implementation of deterministic random bit era in YubiKey’s FIPS-certified {hardware} tokens uncovered cryptographic keys to potential compromise,” Xu identified.
The implications stretch throughout digital safety and will open the doorways for sensible customers of quantum computer systems. Higher random numbers imply stronger encryption keys for all the pieces from on-line banking to authorities functions, messaging apps, and social media. They may additionally make digital signature methods safer, safer crypto wallets, and forestall information tampering for instance.
One explicit use case for licensed randomness is a trustless random beacon: a public service that commonly emits actually random numbers that nobody can predict, manipulate, or pretend—like an common 2FA code generator—and does so in a means that anybody can confirm.
"For blockchains, quantum-certified randomness can energy actually truthful and tamper-proof consensus algorithms, considerably strengthening platforms like Ethereum and Solana in opposition to manipulation," Xu informed Decrypt.
“Wherever that sensible contracts or consensus mechanisms depend on random numbers could possibly be improved in the event that they 'name' a quantum random quantity," Konstantinos Karagiannis, director of quantum computing companies at Protiviti, informed Decrypt.
Public lotteries, playing websites, banking operations, advertising companies that do A/B testing, and bioresearch firms are among the many companies that would drastically profit from utilizing actually random quantity era.
Regardless of its promise, the method continues to be not appropriate for on a regular basis use. The verification stage at the moment requires supercomputing energy that the majority organizations lack, which suggests it’s not well worth the trouble to implement proper now.
Nonetheless, Quantinuum’s Jones suggests the expertise is already transferring towards accessibility, with different gamers engaged on extra sustainable paths.
"Whereas the JPMC analysis required supercomputers for certification, Quantum Origin takes a unique method," he stated. "It leverages Bell exams on a quantum pc to generate a quantum seed (strong-seed). As soon as the quantum seed is generated (a one-time course of), it's embedded into software program and may improve any native random supply to 'quantum' randomness."
The trail to mainstream adoption seems promising, marking the primary time consultants consider quantum computing could have an precise mass utility within the brief time period.
“Chip-scale will possible proceed to get cheaper (and hopefully extra immune to noise). Including them to only about any machine inside this decade could also be attainable” Karagiannis informed Decrypt. It's a imaginative and prescient additionally shared by Xu.
“As for functions on the cloud, numbers generated by actual quantum computer systems could also be available as a part of workloads," Karagiannis added. "It’s possible you’ll at some point add quantum processing items (QPUs) for a number of capabilities, together with random numbers.”
If he's proper, and this method proves profitable, we could ultimately transfer towards an web the place spoofing assaults grow to be mathematically unattainable reasonably than simply tough, making a essentially safer digital world constructed on the bizarre quirks of quantum physics.
Edited by Andrew Hayward


